

Dolby Atmos® and Immersive Audio Mixing

What Is Immersive Audio
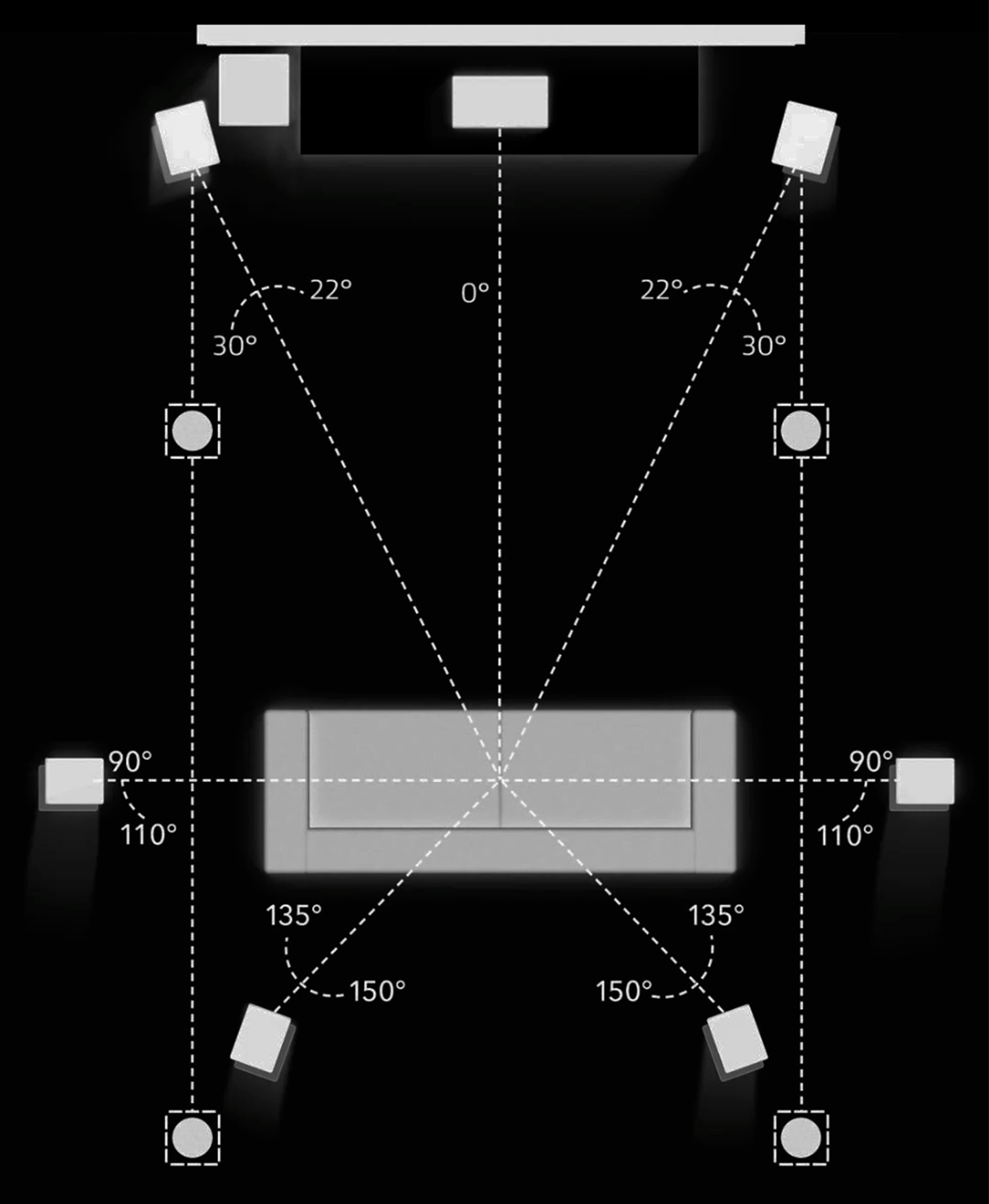
What Is Dolby Atmos
Dolby Atmos is a surround sound technology that creates a more immersive, three-dimensional audio experience. It goes beyond traditional surround sound by adding height channels, allowing sounds to be positioned above and around the listener. This creates a more realistic and engaging soundscape, enhancing movies, music, and games.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
Spatial Sound:
Dolby Atmos utilizes object-based mixing, where individual sounds are treated as objects with defined positions in 3D space. This allows for precise placement and movement of sounds, creating a more dynamic and realistic listening experience.
Height Channels:
Unlike traditional surround sound, Dolby Atmos incorporates overhead channels, often using ceiling-mounted or upward-firing speakers. This adds a layer of height to the soundstage, making it feel like sounds are coming from above as well as around you.
Immersive Experience:
The combination of object-based mixing and height channels creates a more enveloping and immersive sound field. You'll hear sounds move around you, above you, and even seem to come from specific locations within the scene.
Content and Devices:
Dolby Atmos is supported by a wide range of content, including movies, music, and games. Many streaming services and Blu-ray discs offer Dolby Atmos soundtracks. Various devices like soundbars, home theater systems, headphones, and even some smartphones and gaming consoles support Dolby Atmos.
Become Immersed Into The Mix
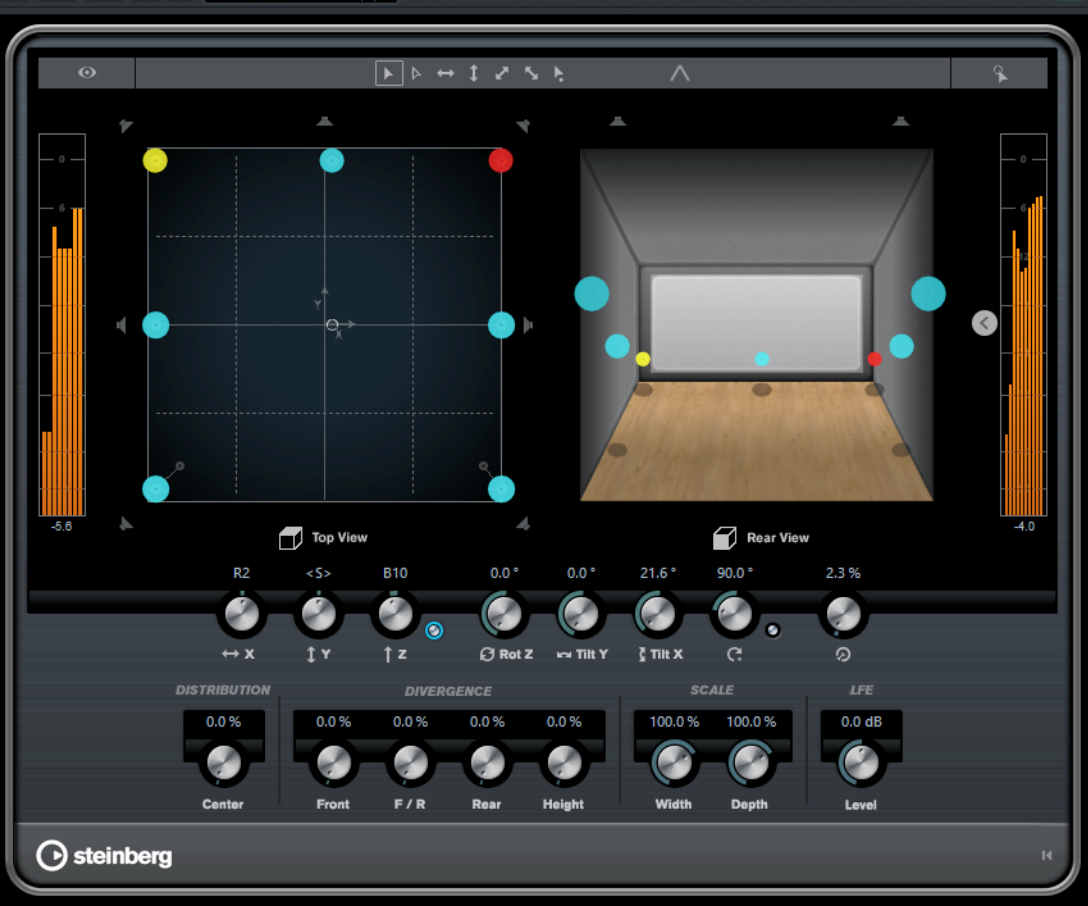
Immersive audio refers to a sound experience that surrounds the listener, creating a sense of depth and space beyond traditional stereo. It utilizes multi-channel speaker setups or object-based mixing techniques to precisely position sounds in a 3D space, enhancing realism and engagement. This technology is used in home theaters, gaming, and music, with formats like Dolby Atmos and Sony 360 Reality Audio gaining popularity.
What Is Ambisonics
Ambisonics is a technology that creates a spherical sound field. Unlike traditional immersive sound formats, it is not channel-based, using an encoded bundle of multiple audio streams to place sounds anywhere within the sound sphere. The precision of positioning depends on the number of streams, described as first, second or third order. Our system supports Ambisonics up to the fourth order. Import pre-produced Ambisonics sound mixes as Wave files and use the internal Ambisonics Panner to create an Ambisonics mix from mono, stereo or surround sources.

Immersive Game Audio with Spatial Sound
Traditional audio, even in 5.1 and 7.1 surround sound, is flat. It only provides audible cues within a 2D environment to the front, back, left, and right of the listener.
Spatial audio, in contrast, gives the illusion that sounds are coming directly from an object in 3-dimensional space, even above or below the player, with pinpoint precision and realism.
This is significant because it means your game can provide total immersion for the gamer. The player can have a wider field of awareness than with visuals alone, which can mean life or death in competitive first-person shooter games. It can also provide anchoring and persistence of objects in the 3D space for games in which the player needs to recognize where the targets and obstacles are or whether they’re being chased by enemy ships from behind.
This level of immersion also helps tell interactive stories more effectively, with realism heightening the player’s senses, such as with spooky sounds in horror games.
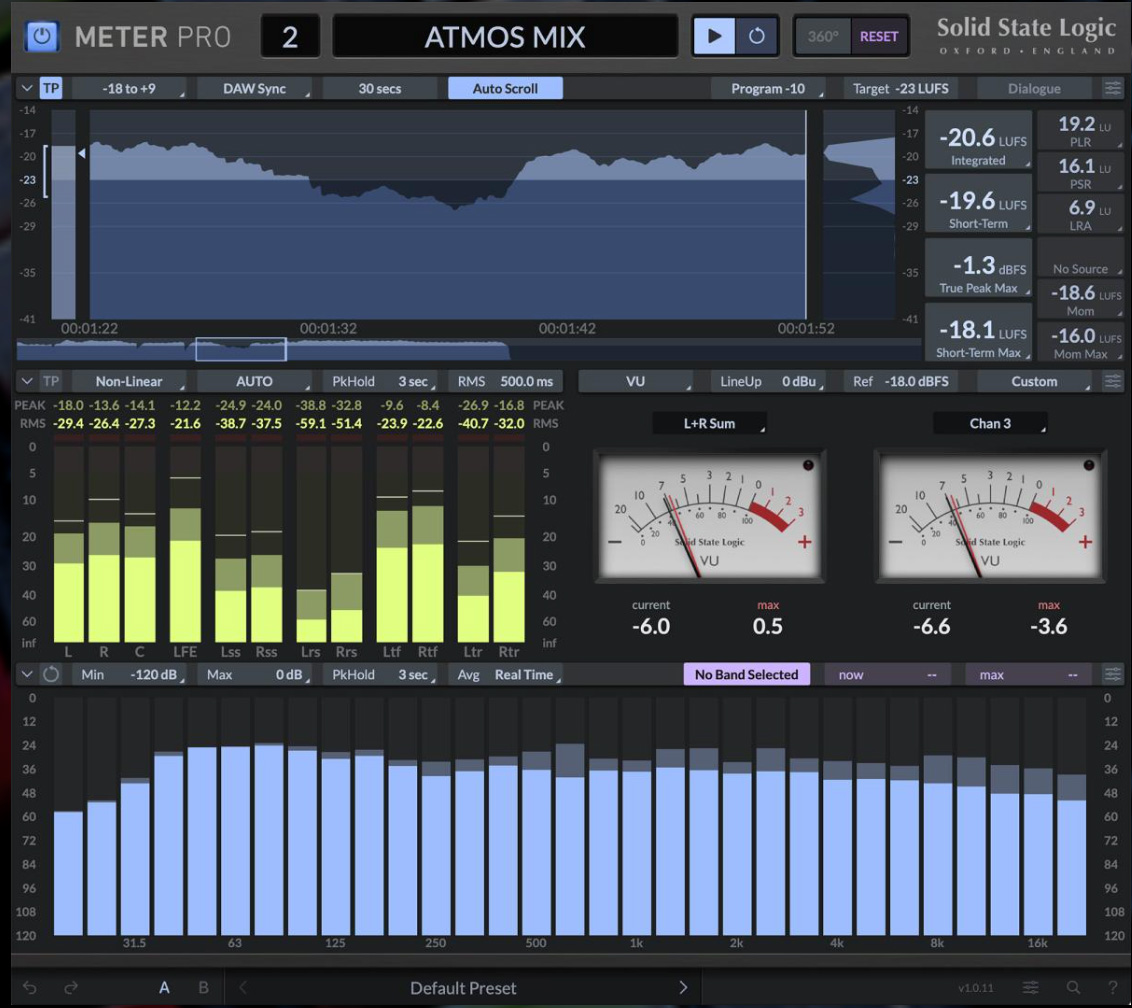
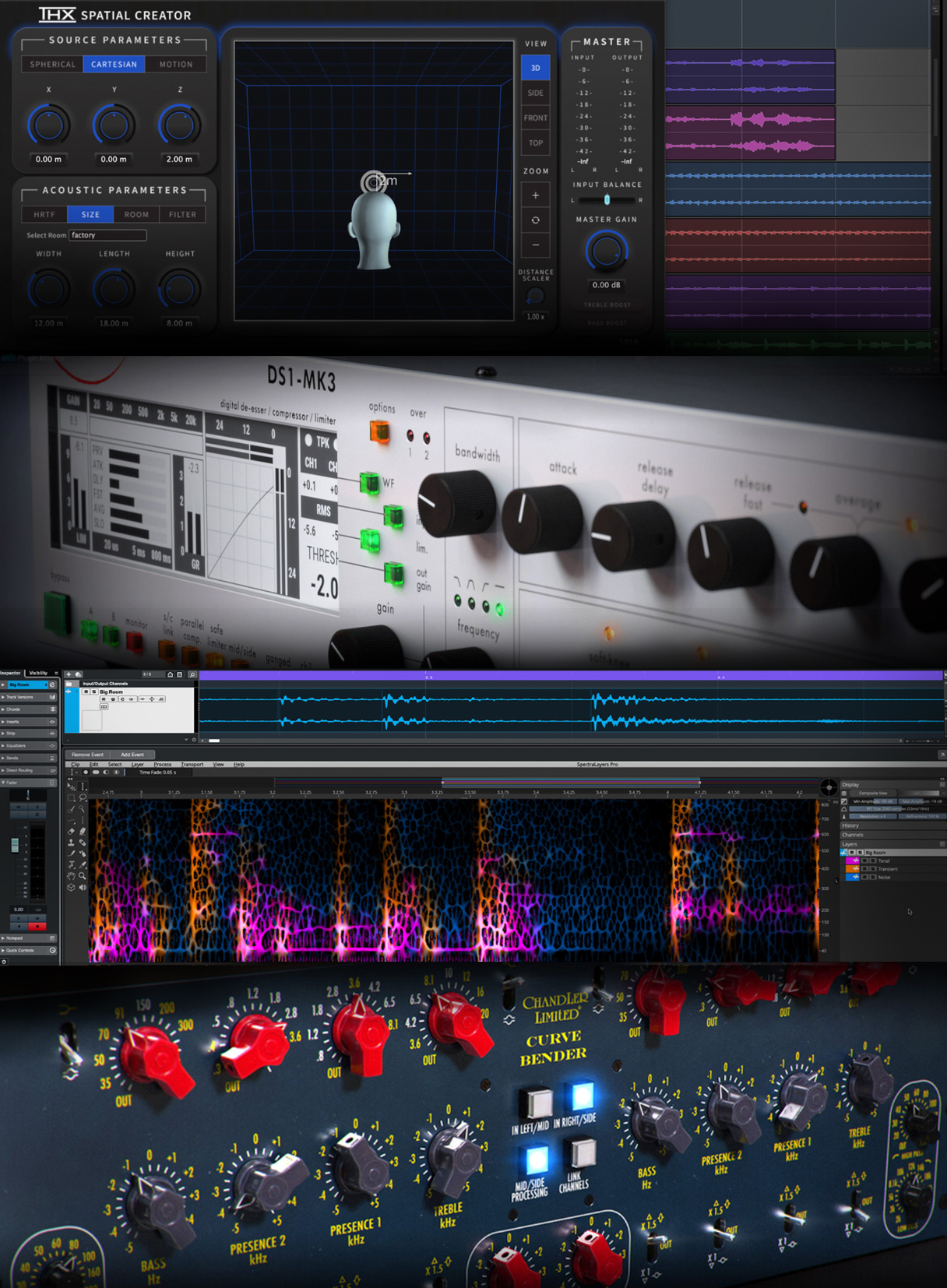
Mastering Services From Stereo To 7.1.4
Mastering For Video
Film Mastering is an intricate process that goes beyond simply balancing audio levels. Mastering for Film, TV, or Video involves a deep understanding of sound design, dialogue clarity, and the various audio formats that are essential in the film and television industry. The importance of mastering cannot be overstated, as it ensures that the final audio product meets industry standards and provides an optimal listening experience for the audience. In this article, we will explore the nuances of mastering specifically tailored for film and television, highlighting the key differences from music mastering and providing techniques that audio engineers can utilize to deliver high-quality soundtracks.
- Loudness Normalisation: Adjusting the overall volume to meet broadcast standards and audience expectations.
- Stereo Widening: Enhancing the stereo image for a fuller sound.
- EQ Adjustments: Making broad frequency adjustments to ensure the mix sounds cohesive.
Fairlight Audio Inside DaVinci Resolve
Mastering For Music
Key aspects of audio mastering:
Enhancement and Optimization:
Mastering engineers use tools like equalization (EQ), compression, and limiting to enhance the overall sound and loudness of a track.
Consistency and Balance:
Mastering ensures that the track sounds balanced and consistent across different playback systems, from headphones to large speakers.
Final Polish:
It provides the final polish to a track, ensuring it's ready for release and sounds its best on various platforms.
Album Sequencing:
In the case of albums, mastering also involves sequencing the tracks and creating a cohesive listening experience.
Final Check:
Mastering is the last stage before the music is released, serving as a final quality control check.
Technical Precision:
Mastering requires a high level of technical expertise and attention to detail, as even small adjustments can significantly impact the final sound.
In essence, mastering takes a finished mix and transforms it into a polished, professional-sounding track ready for the world to hear. It involves fine-tuning the overall sound, optimizing loudness and dynamics, and ensuring consistency across different playback systems. Mastering engineers use techniques like equalization, compression, limiting, and stereo enhancement to achieve a polished and professional sound.
Media vs Music Mastering
While both music and film mastering share the goal of producing high-quality audio, there are significant differences in their approaches. Music mastering focuses primarily on the musical elements, such as rhythm, melody, harmony, tonal balance and dynamics, while mastering for film requires a greater emphasis on dialogue clarity, music level balance, and sound design.
Some key differences include:
- Dialogue Importance: In film, dialogue must be clear and intelligible, often requiring specific adjustments to ensure it stands out amidst background sounds.
- Sound Design Integration: Film mastering involves integrating sound effects and music in a way that complements the visuals, which is less of a concern in music mastering.
- Dynamic Range: Films often require a broader dynamic range to accommodate quiet dialogue and loud action sequences, whereas music may be more uniform in its dynamics.
For More Information About Rates and Bookings Call Mike Green @ 615.881.5648 • Email • synthetikasound@gmail.com
© 2025 Synthetika Sound LLC • Hendersonville, TN